Difference between revisions of "Reference:Gradient Pattern"
Le Forgeron (talk | contribs) |
m (canonicalize some version numbers) |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
the x location increases it smoothly turns to the last color at x=1. Then it | the x location increases it smoothly turns to the last color at x=1. Then it | ||
starts over with the first again and gradually turns into the last color at | starts over with the first again and gradually turns into the last color at | ||
| − | x=2. In POV-Ray versions older than | + | x=2. In POV-Ray versions older than v3.5 the pattern reverses for negative values of x. |
| − | As per POV-Ray | + | As per POV-Ray v3.5 this is not the case anymore. Using <code>gradient |
y</code> or <code>gradient z</code> makes the colors blend along the y- or | y</code> or <code>gradient z</code> makes the colors blend along the y- or | ||
z-axis. Any vector may be used but x, y and z are most common.</p> | z-axis. Any vector may be used but x, y and z are most common.</p> | ||
Latest revision as of 14:54, 9 June 2021
One of the simplest patterns is the gradient pattern. It is
specified as
pigment {
gradient <Orientation>
[PIGMENT_MODIFIERS...]
}
where <Orientation> is a vector pointing in
the direction that the colors blend. For example
pigment { gradient x } // bands of color vary as you move
// along the "x" direction.
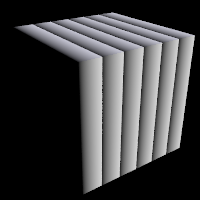
produces a series of smooth bands of color that look like layers of colors
next to each other. Points at x=0 are the first color in the color map. As
the x location increases it smoothly turns to the last color at x=1. Then it
starts over with the first again and gradually turns into the last color at
x=2. In POV-Ray versions older than v3.5 the pattern reverses for negative values of x.
As per POV-Ray v3.5 this is not the case anymore. Using gradient
y or gradient z makes the colors blend along the y- or
z-axis. Any vector may be used but x, y and z are most common.
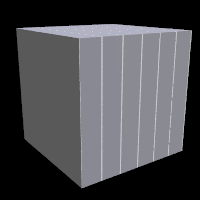
As a normal pattern, gradient generates a saw-tooth or ramped wave appearance. The syntax is
normal {
gradient <Orientation> [, Bump_Size]
[NORMAL_MODIFIERS...]
}
where the vector <Orientation> is a required
parameter but the float Bump_Size which follows is
optional.
Note: The comma is required especially if Bump_Size is negative.
If only the range -1 to 1 was used of the old gradient, for example in a
sky_sphere, it can be replaced by the planar or marble
pattern and revert the color_map. Also rotate the pattern for other orientations than y.
A more general solution is to use function{abs(x)} as a pattern instead
of gradient x and similar for gradient y and gradient z.
gradient pattern used as pigment and normal respectively |
|